Qatar History Timeline: Major Milestones
Qatar holds an essential position for researchers interested in ancient civilizations and historical events in the Gulf region. This small country is located in the heart of the Arabian Gulf, serving as a cultural bridge that connects the civilizations of Mesopotamia, the Red Sea, and the Indian Ocean. When we speak of Qatar history, we tell a story that spans thousands of years, the story of a people who adapted to harsh living conditions and wove a distinctive civilization. Today, Qatar presents itself as a modern cultural and tourist destination with deep roots in history, attracting visitors from around the world who wish to understand its remarkable development and explore the country’s tourism offerings.
Enjoy your trip with almatar without limits
Are you planning to visit Qatar or any country around the world? almatar offers the extra baggage service, where you can obtain this feature for all passengers or for a single traveler, ensuring a comfortable and worry-free journey. Pack your bags freely and get ready to explore the world.
The most essential milestones in Qatar history
-
The Ancient Era: The Birth of Civilization in the Gulf
Early Settlements
Archaeological excavations and discoveries by researchers indicate that the land of Qatar has been inhabited since approximately 5,000 BC. This means that the formation of Qatar as a geographic area where people lived dates back to very ancient times, where small communities survived on fishing and herding. Researchers also discovered engravings, stone tools, and pottery crafted with great skill, indicating the presence of organized and developed cultural activity.
Qatar’s Connection with the Ubaid Civilization
During the Ubaid period (approximately 6000–3800 BC), Qatar was influenced by commercial and cultural activities originating from southern Iraq. It formed one of the stations in the exchange network across the Arabian Gulf. The influence of the Ubaid civilization extended from south Mesopotamia to the Arabian Gulf regions, including the Qatar Peninsula. Excavations revealed fine pottery and carefully crafted tools, reflecting cultural and artistic contact with Ubaid centers in southern Iraq, providing necessary evidence for the study of Qatar traditions.
Early Greek References to Qatar and Its Maritime Role
In classical times, the Greek geographer Ptolemy, in the second century AD, referred to a region on the western coast of the Arabian Gulf named “Catara,” the earliest known documentation of the name “Qatar” in ancient sources. Research indicates that the coasts of Qatar have been centers of maritime and trade activity since ancient times, connected to the civilizations of Mesopotamia and the Gulf, particularly during the Persian and Greek influences.
-
The Islamic Era: A Civilizational Turning Point
After the emergence of Islam in the seventh century AD, many eastern regions of the Arabian Peninsula joined the new Islamic state. These regions played a crucial role in the Islamic conquests, as their people contributed to the preparation of naval fleets. Under the Rashidun, Umayyad, and Abbasid caliphates, Qatar experienced significant economic prosperity, particularly during the Abbasid period, when trade and economic life flourished across the region.
-
The Ottoman and Portuguese Era: Competition of Powers
Maritime Conflict
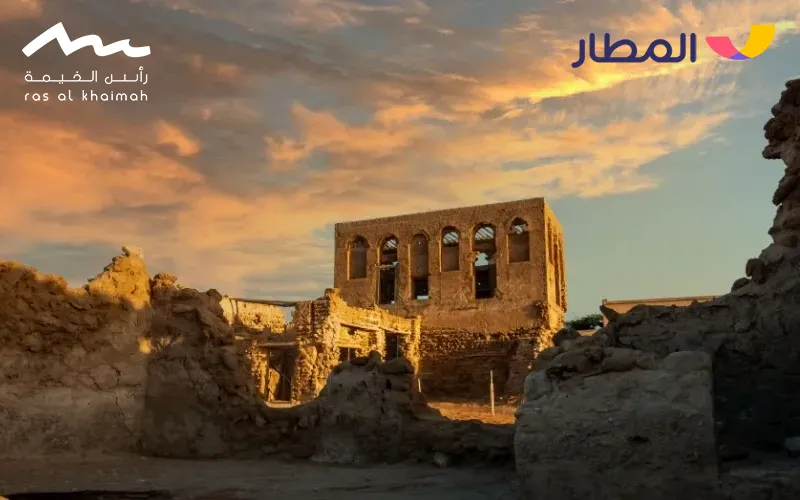
In the sixteenth century AD (the tenth Hijri century), Portuguese influence reached the Gulf coasts, and Qatar was affected by the conflict between them and the Ottomans, who sought to establish their presence in the region. Over time, Qatar experienced intermittent Ottoman control, the last of which was in the late nineteenth century when the Ottomans sent a garrison to Doha in 1871. However, this control was mainly nominal, as local rule remained in the hands of tribal sheikhs until the Ottoman withdrawal in 1915, a chapter frequently mentioned in Qatar history studies.
-
The Period of Rise: The Eighteenth and Nineteenth Centuries
The Emergence of the Commercial Town of Al Zubarah
In the late eighteenth century, the Arabian Gulf experienced significant political and commercial shifts, with the emergence of new ports replacing older centers. During that time, merchant families migrated from eastern Arabia and Basra to the city of Al Zubarah in northern Qatar, which quickly became a thriving port and a hub of economic exchange in the Gulf. Al Zubarah became famous for its pearl and Arabian horse trade, and its prosperity contributed to the growing importance of Qatar in regional trade and heritage, making it one of the key Qatar tourist attractions.
The Era of Diving and Pearling
During the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries, Qatari culture was deeply tied to the sea. People practiced fishing and diving for pearls, which formed the region’s primary source of wealth. This demanding and dangerous profession shaped the character of Qatari society. It helped form its economic and social identity for many decades, leaving a lasting mark on Qatar traditions and daily life.
To learn more about the culture and Qatar traditions, read the following article:
Qatar Culture and Traditions: How the Past Shapes the Present
-
The Unification and Modern Foundation: The Era of Al Thani
Sheikh Mohammed bin Thani: The Foundation of Modern Qatar
In the mid-nineteenth century, Sheikh Mohammed bin Thani emerged as one of Qatar’s most prominent leaders, distinguished by his wisdom and ability to unite the scattered Qatari tribes. He is considered the first to lay the foundations of modern Qatar as a political entity, successfully establishing internal stability and maintaining balanced relations with regional powers. During his rule, national identity awareness grew. In 1868, he signed an agreement with Britain to regulate maritime peace in the Gulf, distinguishing Qatar as a political entity independent from its neighbors and marking a milestone in Qatar history.
-
The Modern Era: From Protection to Independence
The British Protection Treaty (1916)
After the Ottomans withdrew from Qatar in 1915 and their empire collapsed following World War I, Sheikh Abdullah bin Jassim Al Thani signed a treaty with Britain in 1916. This treaty guaranteed Qatar’s protection from external aggression and shaped the next stage in its modern governance.
Discovery of Oil: The Turning Point
The first oil well in Qatar was drilled in October 1938; however, production ceased due to World War II. Export resumed in 1949 through Mesaieed Port, marking the shift from a pearl-based and maritime economy to a modern oil economy that completely transformed the nation’s landscape, another critical stage for tourism in Qatar and economic development alike.
Complete Independence (1971)
On September 3, 1971, Sheikh Ahmed bin Ali Al Thani declared Qatar’s complete independence from Britain. In the same month, Qatar joined the Arab League and the United Nations. In February 1972, Sheikh Khalifa bin Hamad Al Thani assumed power, initiating the phase of building modern state institutions and enhancing Qatar’s regional and international role.
-
Contemporary Development: The Journey of Modernization
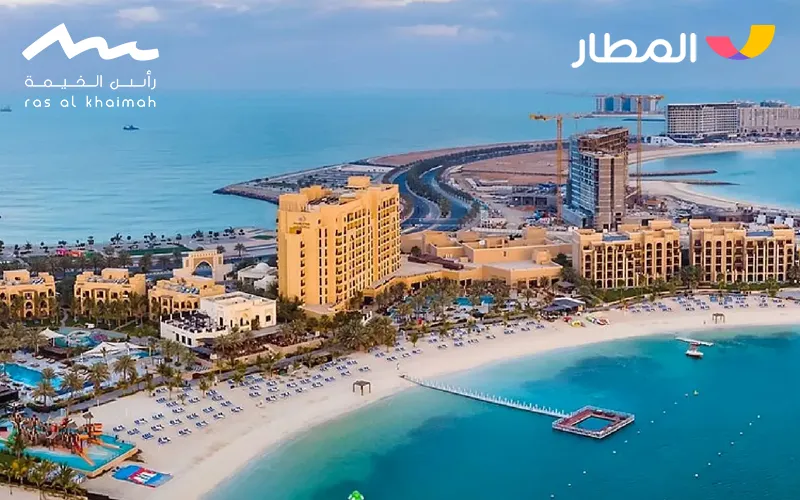
With its wealth of oil and natural gas, Qatar wisely invested in infrastructure, education, and healthcare. Doha became a modern city that still preserves its heritage. Qatar hosted major global events, such as the 2022 FIFA World Cup, transforming it into a thriving oasis of economic vitality and investment, as well as a hub for tourism in Qatar. The country today boasts a blend of desert landscapes, stunning coastlines, and impressive facilities with strong, modern infrastructure that highlight Qatar tourist attractions worldwide.
Get Exclusive Privileges with “Jawwak” from almatar
Before ending your meaningful exploration, especially if you are planning a trip in Qatar, don’t hesitate to benefit from almatar’s loyalty program: Jawwak. This program offers you exclusive points, discounts, special rates, and early deals, making your journey both economical and comfortable. Collect points with every booking and enjoy VIP privileges.
Conclusion
Qatar’s journey through time is a living testimony to human resilience and progress. From the ancient civilizations that passed along its shores to the era of diving and trade, and finally to the modern, advanced state, Qatar stands as a model of evolution and endurance. Today, it opens its doors to tourists from around the world to discover this cultural monument and its rich Qatar history through its museums, archaeological sites, and carefully designed Qatar tourist attractions.
Frequently Asked Questions about Qatar History
When did Qatar gain independence?
Qatar declared its complete independence from Britain on September 3, 1971.
How did Qatar’s economy change?
The Qatari economy transformed from one based on pearl diving and fishing in the past centuries to an oil-based economy after the discovery of oil and gas, with exports starting in 1949.
What makes Qatar a vital tourist destination today?
Qatar combines ancient archaeological sites, modern museums, contemporary architecture, and advanced infrastructure, offering a delightful and exciting experience for lovers of history and tourism in Qatar.
Are there significant historical sites to visit in Qatar?
Yes, there are several significant sites such as Al Zubarah Fort, the National Museum, and the archaeological city of Al Zubarah, all of which reflect the depth of Qatar traditions and heritage.